

Deploying applications efficiently is a critical part of modern development workflows. Paketo Buildpacks offer a powerful way to build and deploy applications using a consistent and reliable approach. In this tutorial, we will guide you through the process of deploying Paketo Buildpacks on Docker using Ubuntu 24.04. This guide is designed for beginners and will provide detailed instructions for setting up Docker, building applications with Paketo Buildpacks, and running your applications in Docker containers.
1. Introduction to Docker and Paketo Buildpacks
What is Docker?
Docker is a platform that allows you to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of applications using containerization. Containers are lightweight, portable, and ensure that applications run consistently across different environments. Docker simplifies the process of setting up complex environments, making it easier to share and collaborate.
What are Paketo Buildpacks?
Paketo Buildpacks are a set of open-source buildpacks that provide a consistent way to build applications into container images. They detect the language and framework of your application, install the necessary dependencies, and configure your application for optimal performance in a containerized environment. Paketo Buildpacks support a variety of languages and frameworks, including Java, Node.js, Python, and more.
2. Installing Docker on Ubuntu 24.04
Before we can deploy applications with Paketo Buildpacks, we need to install Docker on our Ubuntu 24.04 system. Follow these steps to get Docker up and running:
Step 1: Update Your System
First, update your system to ensure all packages are up to date. Open a terminal and run:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade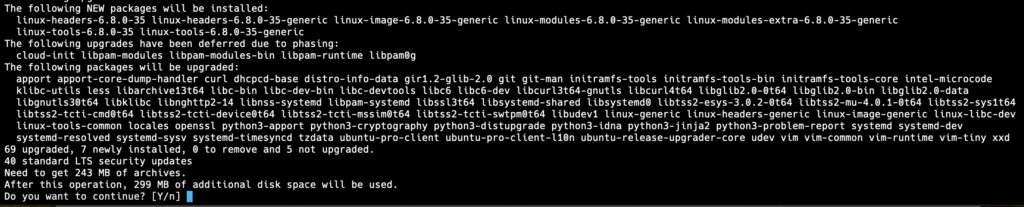
Step 2: Install Docker
Ubuntu 24.04 includes Docker in its official repositories. To install Docker, run the following commands:
sudo apt install docker.io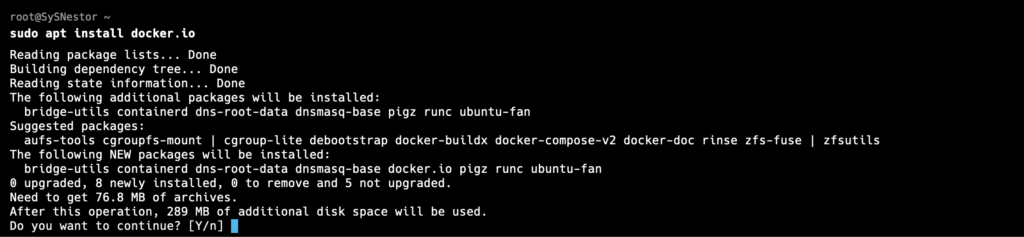
Step 3: Start and Enable Docker
After installation, start the Docker service and enable it to start on boot:
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable dockerStep 4: Verify Docker Installation
To verify that Docker is installed correctly, run:
docker --version
Step 5: Add User to Docker Group
To run Docker commands without sudo, add your user to the Docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER3. Setting Up Paketo Buildpacks
Now that Docker is installed, we can set up Paketo Buildpacks. Paketo Buildpacks can be used with the pack CLI, which helps build applications into container images.
Step 1: Install the Pack CLI
To install the pack CLI, follow these steps:
- Download the Pack CLI:
curl -sSL "https://github.com/buildpacks/pack/releases/download/v0.28.0/pack-v0.28.0-linux.tgz" | tar -xzv- Move the Pack CLI to a Directory in Your PATH:
sudo mv pack /usr/local/bin/pack- Verify the Installation:
pack --version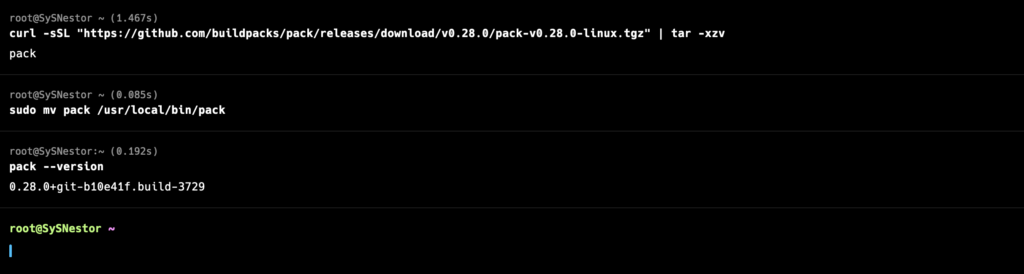
You should see the version of pack installed.
4. Building an Application with Paketo Buildpacks
To demonstrate how to use Paketo Buildpacks, we will create a simple Node.js application and build it into a container image.
Step 1: Create a Node.js Application
First, create a directory for your project:
mkdir paketo-node-app
cd paketo-node-app
sudo apt install nodejs npmInitialize a new Node.js application:
npm init -y
Install Express.js as a dependency:
npm install express
Create an index.js file with the following content:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, Paketo Buildpacks!');
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${port}`);
});Step 2: Create a Dockerfile
Although Paketo Buildpacks can build an application without a Dockerfile, it’s useful to see the typical structure. Create a Dockerfile in your project directory:
touch Dockerfile
nano DockerfileAdd the following content to the Dockerfile:
# Use Paketo Buildpack for Node.js
FROM paketobuildpacks/builder:base
# Set the working directory
WORKDIR /workspace
# Copy application files
COPY . /workspace
# Use Paketo Buildpacks to build the application
RUN pack build my-paketo-node-app --builder paketobuildpacks/builder:baseStep 3: Build the Application
Use the pack CLI to build your application:
pack build my-paketo-node-app --builder paketobuildpacks/builder:base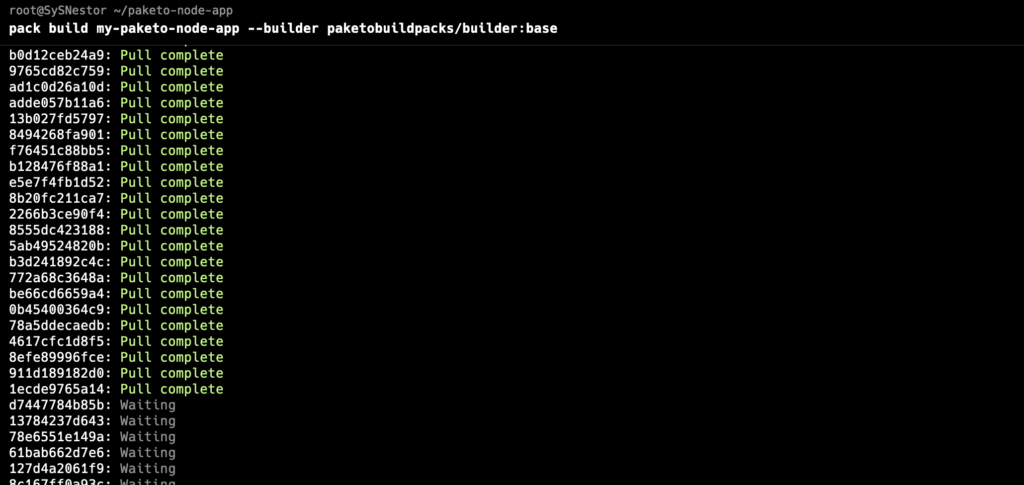
This command will detect the language and framework of your application, install the necessary dependencies, and create a container image named my-paketo-node-app.
5. Running and Managing the Application Container
Step 1: Run the Container
Run the container using the Docker run command:
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name my-paketo-node-app-container my-paketo-node-appThis command runs the container in detached mode (-d), maps port 3000 on your host to port 3000 in the container (-p 3000:3000), and names the container my-paketo-node-app-container.
Step 2: Verify the Application
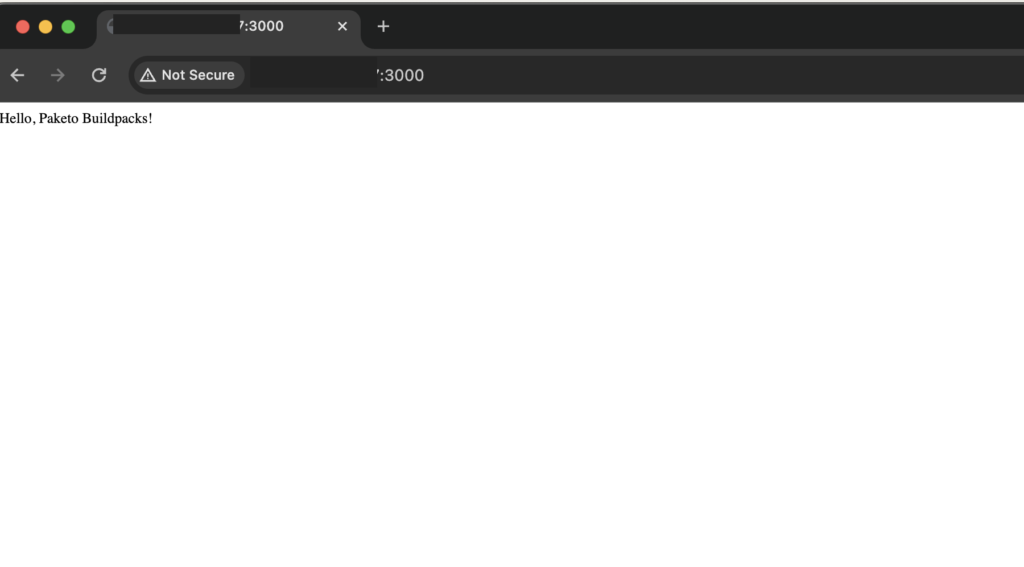
Open your web browser and go to http://localhost:3000. You should see the message “Hello, Paketo Buildpacks!”.
Step 3: Viewing Container Logs
To see the logs from the running container, use the docker logs command:
docker logs my-paketo-node-app-containerStep 4: Accessing the Container
To open a bash shell inside the running container, use the docker exec command:
docker exec -it my-paketo-node-app-container bashStep 5: Stopping and Restarting the Container
To stop the running container, use the docker stop command:
docker stop my-paketo-node-app-containerTo restart the container, use the docker start command:
docker start my-paketo-node-app-containerStep 6: Removing the Container
If you no longer need the container, you can remove it using the docker rm command:
docker rm my-paketo-node-app-containerDeploying applications with Paketo Buildpacks on Docker using Ubuntu 24.04 is a powerful and efficient way to manage your development and production environments. Docker ensures consistency and ease of sharing, while Paketo Buildpacks automate the build process, making it simple to create optimized container images.
In this tutorial, we covered the basics of Docker, how to install Docker on Ubuntu 24.04, and how to use Paketo Buildpacks to build and run a Node.js application in a Docker container. With this knowledge, you can now explore more advanced features of Docker and Paketo Buildpacks, customizing your environment to meet your specific needs.
Happy coding! If you have any questions or run into any issues, feel free to leave a comment below.
